La Battaglia d'Inghilterra - Myouth - Ricordi degli anni '70
Menu principale:
La Battaglia d'Inghilterra
Modellismo > Aerei > Supermarine Spitfire Mk.1
La Battaglia d'Inghilterra
Battle of Britain

Osservatore aereo nella Battaglia d'Inghilterra
Battle of Britain air observer

Bombardieri Heinkel He 111 durante la battaglia di Inghilterra.
Heinkel He 111 Bombers during the Battle of Britain

Gli Spitfire
Spitfires

Lo Junkers Ju 88, il primo aereo della Luftwaffe a effettuare un'incursione in Gran Bretagna.
Junkers Ju 88, the first Luftwaffe plane that did a raid over Britain
La battaglia d'Inghilterra (in inglese: Battle of Britain e in tedesco: Luftschlacht um England) è il nome storico della campagna aerea svoltasi durante la seconda guerra mondiale e combattuta dall'aeronautica militare tedesca, la Luftwaffe, contro il Regno Unito tra l'estate e l'autunno del 1940. L'obiettivo della campagna era di guadagnare la superiorità aerea sull'aviazione militare britannica, la Royal Air Force (RAF), e particolarmente contro i suoi aerei da caccia inquadrati nel RAF Fighter Command.
La battaglia d'Inghilterra fu la prima grande campagna di guerra a essere combattuta interamente da forze aeree e fu anche la più grande e intensa azione di bombardamento aereo fino a
quella data. Nel luglio 1940, gli obiettivi principali furono i
convogli di rifornimento e i porti, quali Portsmouth; un mese dopo, la Luftwaffe iniziò a colpire gli aeroporti e le infrastrutture della RAF. Con il progredire della battaglia, la Luftwaffe
iniziò a bombardare anche le fabbriche aeronautiche e altre
infrastrutture, anche per annientare la volontà di resistenza della
popolazione civile. Alla fine, la Luftwaffe si concentrò su aree di significato politico utilizzando la strategia del bombardamento strategico.
Il fatto che la Germania nazista fallì nei suoi piani non riuscendo né a distruggere il sistema di difesa aerea britannico, né a obbligare il Regno Unito a negoziare un armistizio
o una resa, è considerato la prima significativa sconfitta tedesca
della seconda guerra mondiale e un punto di svolta cruciale
nell'andamento del conflitto. Impedendo alla Germania di acquisire la superiorità aerea, la battaglia pose fine alla minaccia che Hitler desse il via all'Operazione Leone marino, l'invasione della Gran Bretagna condotta da un attacco anfibio e con il lancio dei Fallschirmjäger, i paracadutisti.
Alla battaglia partecipò anche la Regia Aeronautica con 170 tra caccia, bombardieri e ricognitori, inquadrati nel C.A.I., Corpo Aereo Italiano.
Fonte: Wikipedia
The Battle of Britain (German: Luftschlacht um England, literally "The Air Battle for England") was a military campaign of the Second World War, in which the Royal Air Force (RAF) defended the United Kingdom (UK) against large-scale attacks by Nazi Germany's air force, the Luftwaffe. It has been described as the first major military campaign fought entirely by air forces. The British officially recognise the battle's duration as being from 10 July until 31 October 1940, which overlaps the period of large-scale night attacks known as The Blitz, that lasted from 7 September 1940 to 11 May 1941. German historians do not accept this subdivision and regard the battle as a single campaign lasting from July 1940 to June 1941, including the Blitz.
The primary objective of the German forces was to compel Britain to agree to a negotiated peace settlement. In July 1940, the air and sea blockade began, with the Luftwaffe mainly targeting coastal-shipping convoys, ports and shipping centres, such as Portsmouth. On 1 August, the Luftwaffe was directed to achieve air superiority over the RAF with the aim of incapacitating RAF Fighter Command; 12 days later, it shifted the attacks to RAF airfields and infrastructure. As the battle progressed, the Luftwaffe also targeted factories involved in aircraft production and strategic infrastructure. Eventually, it employed terror bombing on areas of political significance and on civilians.
The Germans had rapidly overwhelmed France and the Low Countries, leaving Britain to face the threat of invasion by sea. The German high command knew the difficulties of a seaborne attack and its impracticality while the Royal Navy controlled the English Channel and the North Sea. On 16 July, Adolf Hitler ordered the preparation of Operation Sea Lion as a potential amphibious and airborne assault on Britain, to follow once the Luftwaffe had air superiority over the UK. In September, RAF Bomber Command night raids disrupted the German preparation of converted barges, and the Luftwaffe's failure to overwhelm the RAF forced Hitler to postpone and eventually cancel Operation Sea Lion. Germany proved unable to sustain daylight raids, but their continued night-bombing operations on Britain became known as the Blitz.
Historian Stephen Bungay cited Germany's failure to destroy Britain's air defences to force an armistice (or even outright surrender) as the first major German defeat in World War II and a crucial turning point in the conflict. The Battle of Britain takes its name from a speech given by Prime Minister Winston Churchill to the House of Commons on 18 June: "What General Weygand called the 'Battle of France' is over. I expect that the Battle of Britain is about to begin."
Source: Wikipedia

Atterraggio di emergenza in spiaggia di un Messerschmitt Bf 109 tedesco.
Emergency landing of a German Messerschmitt Bf 109 on a beach
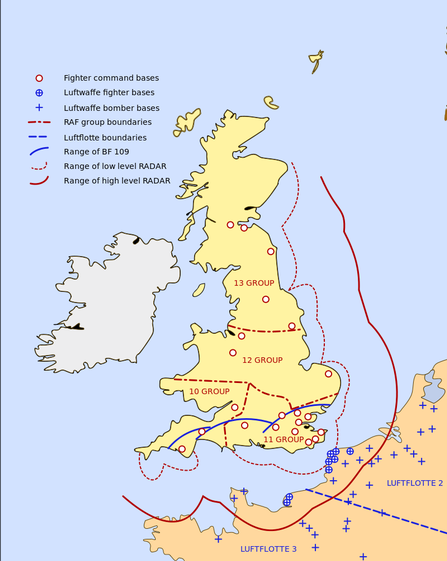
La mappa mostra le basi inglesi e tedesche e la zona coperta dai radar.
Tha map shows English and German bases, and areas covered by radars
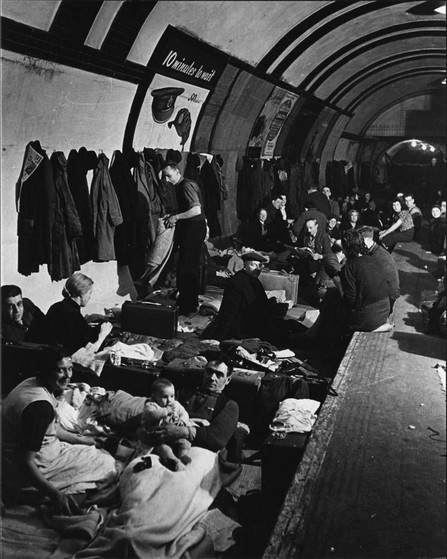

Una stazione della metropolitana di Londra usata come rifugio antiaereo.
London tube station, used as an anti-aircraft refuge
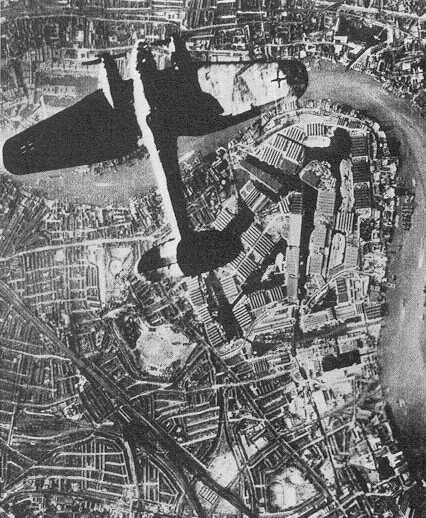

Un fotomontaggio della propaganda nazista mostra un He 111 sui Docks di Londra.
A photomontage of Nazi propaganda shows a He 111 on the London Docks.

Vigili del fuoco mentre cercano di domare un incendio causato dai bombardamenti
Firemen trying to fight fires caused by bombings

Danni a Londra a seguito dei bombardamenti.
London damaged by bombings
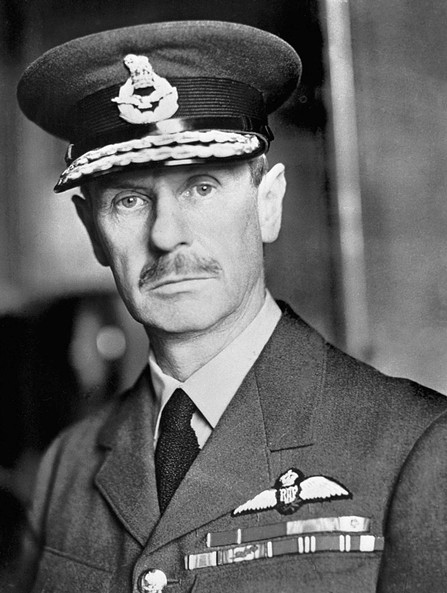

Hugh Dowding, comandante del Comando Caccia della RAF.
Hugh Dowding, Commander of RAF Fighter Command.
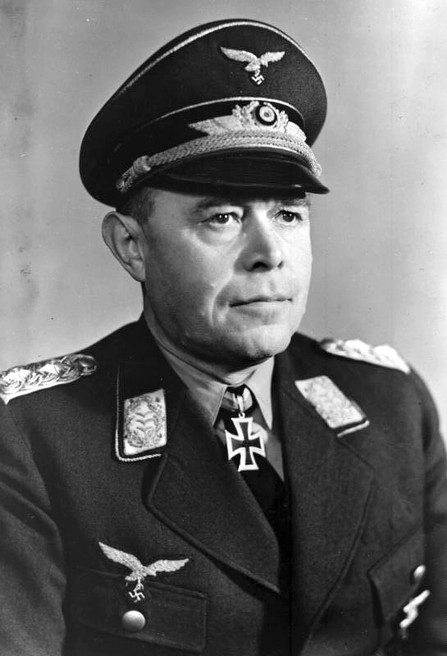

Albert Kesselring, generale tedesco protagonista della battaglia.
Albert Kesselring, German General leading the Battle.
Home Page | Modellismo | Topolini | Altri Disney | Linus | Asterix | Diabolik | Giornalini di guerra | Western | Riviste | Romanzi | Mappa generale del sito